There are four general types (most common categories) of NoSQL databases. Each of these categories has its own specific attributes and limitations. There is not a single solutions which is better than all the others, however there are some databases that are better to solve specific problems. To clarify the NoSQL databases, lets discuss the most common categories :
- Key-value stores
- Column-oriented
- Graph
- Document oriented
Key-value stores
- Key-value stores are most basic types of NoSQL databases.
- Designed to handle huge amounts of data.
- Based on Amazon’s Dynamo paper.
- Key value stores allow developer to store schema-less data.
- In the key-value storage, database stores data as hash table where each key is unique and the value can be string, JSON, BLOB (basic large object) etc.
- A key may be strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets and values are stored against these keys.
- For example a key-value pair might consist of a key like "Name" that is associated with a value like "Robin".
- Key-Value stores can be used as collections, dictionaries, associative arrays etc.
- Key-Value stores follows the 'Availability' and 'Partition' aspects of CAP theorem.
- Key-Values stores would work well for shopping cart contents, or individual values like color schemes, a landing page URI, or a default account number.
Example of Key-value store DataBase : Redis, Dynamo, Riak. etc.
Pictorial Presentation :
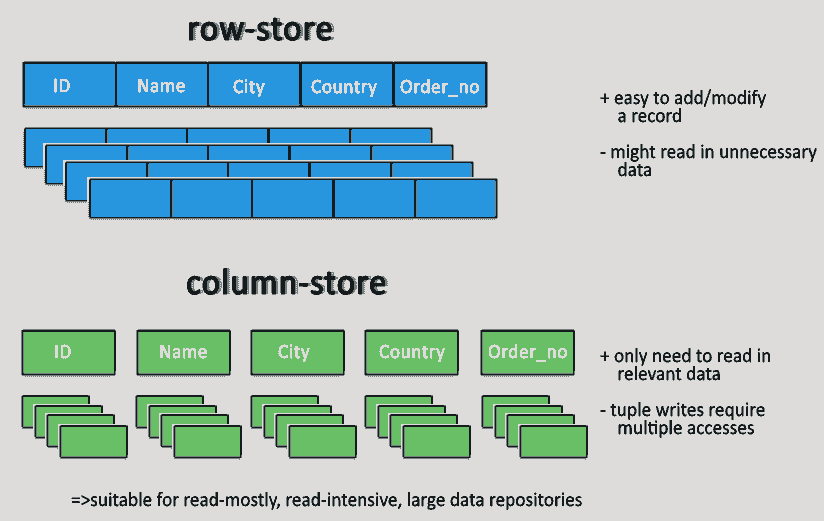
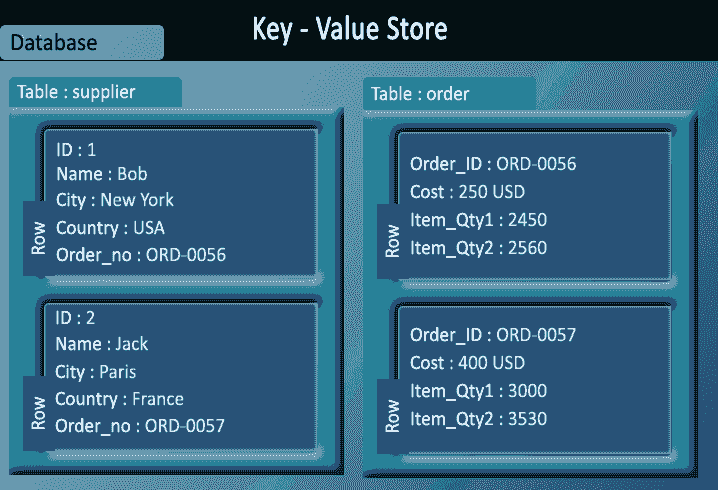
Column-oriented databases
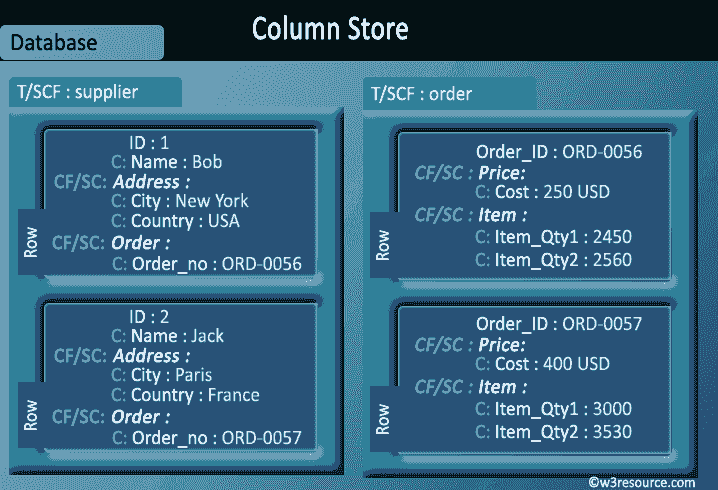
- Column-oriented databases primarily work on columns and every column is treated individually.
- Values of a single column are stored contiguously.
- Column stores data in column specific files.
- In Column stores, query processors work on columns too.
- All data within each column datafile have the same type which makes it ideal for compression.
- Column stores can improve the performance of queries as it can access specific column data.
- High performance on aggregation queries (e.g. COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX).
- Works on data warehouses and business intelligence, customer relationship management (CRM), Library card catalogs etc.
Example of Column-oriented databases : BigTable, Cassandra, SimpleDB etc.
Pictorial Presentation :
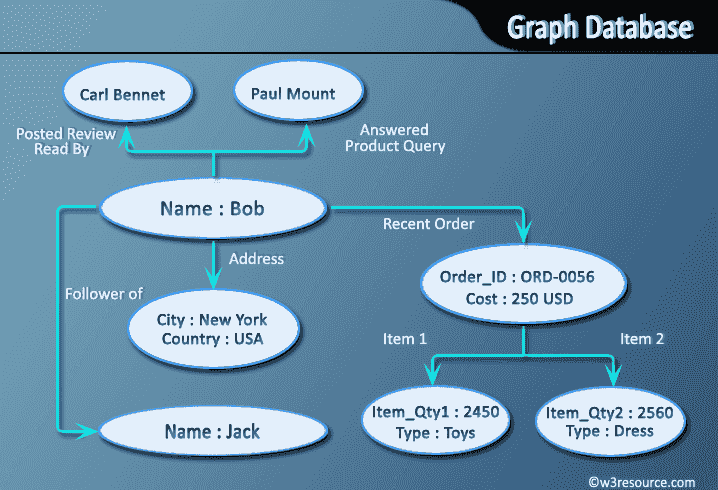
Graph databases
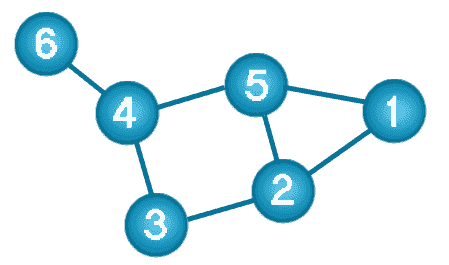
A graph data structure consists of a finite (and possibly mutable) set of ordered pairs, called edges or arcs, of certain entities called nodes or vertices.
Following picture presents a labeled graph of 6 vertices and 7 edges.
What is a Graph Databases?
- A graph database stores data in a graph.
- It is capable of elegantly representing any kind of data in a highly accessible way.
- A graph database is a collection of nodes and edges
- Each node represents an entity (such as a student or business) and each edge represents a connection or relationship between two nodes.
- Every node and edge is defined by a unique identifier.
- Each node knows its adjacent nodes.
- As the number of nodes increases, the cost of a local step (or hop) remains the same.
- Index for lookups.
Here is a comparison between the classic relational model and the graph model :
| Relational model | Graph model |
|---|---|
| Tables | Vertices and Edges set |
| Rows | Vertices |
| Columns | Key/value pairs |
| Joins | Edges |
Example of Graph databases : OrientDB, Neo4J, Titan.etc.
Pictorial Presentation :
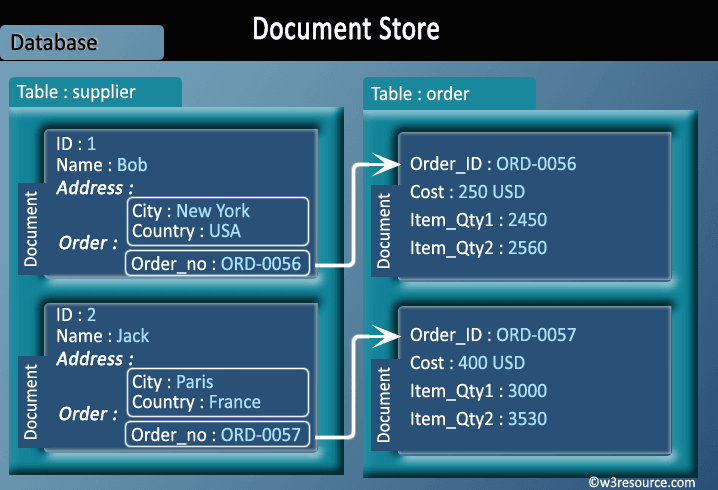
Document Oriented databases
- A collection of documents
- Data in this model is stored inside documents.
- A document is a key value collection where the key allows access to its value.
- Documents are not typically forced to have a schema and therefore are flexible and easy to change.
- Documents are stored into collections in order to group different kinds of data.
- Documents can contain many different key-value pairs, or key-array pairs, or even nested documents.
Here is a comparison between the classic relational model and the document model :
| Relational model | Document model |
|---|---|
| Tables | Collections |
| Rows | Documents |
| Columns | Key/value pairs |
| Joins | not available |
Example of Document Oriented databases : MongoDB, CouchDB etc.
Pictorial Presentation :
No comments:
Post a Comment